Ginger root benefits extend far beyond its well-known ability to calm upset stomachs. This ancient medicinal spice offers powerful anti-inflammatory effects, pain relief, brain protection, and metabolic support backed by over 500 scientific studies.
Whether you’re dealing with nausea, arthritis pain, muscle soreness, or chronic inflammation, ginger provides evidence-based therapeutic benefits that rival many pharmaceutical drugs with an excellent safety profile.
This comprehensive guide explores 12 science-backed ginger root benefits, optimal dosages, best forms (fresh vs powder vs extract), and how ginger compares to other anti-inflammatory herbs.
Key Takeaway: Ginger contains potent bioactive compounds (gingerols and shogaols) that reduce inflammation, relieve pain, support digestion, and protect against chronic disease. Clinical studies show effectiveness for nausea (75% reduction), arthritis pain (comparable to NSAIDs), and muscle soreness (25-50% reduction).
What Is Ginger Root?

Ginger (Zingiber officinale) is a flowering plant native to Southeast Asia, cultivated for its underground rhizome (root) used both as a spice and medicine for over 5,000 years.
Active Compounds in Ginger
Gingerols (Fresh Ginger):
- Primary bioactive compound
- Responsible for pungent taste
- Powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant
- 6-gingerol is most abundant and studied
Shogaols (Dried/Cooked Ginger):
- Formed when gingerols are dried or heated
- Even more potent anti-inflammatory than gingerols
- 6-shogaol has strongest pain-relieving properties
- Concentrated in dried ginger and supplements
Other Active Compounds:
- Paradols (antioxidant, anti-inflammatory)
- Zingerone (antioxidant, digestive aid)
- Essential oils (aromatic, antimicrobial)
Why This Matters: Fresh and dried ginger have different compound profiles, making them suited for different purposes. Research from Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry shows dried ginger has higher shogaol content and stronger anti-inflammatory effects.
12 Science-Backed Ginger Root Benefits
1. Powerful Anti-Nausea and Vomiting Relief ⭐ PRIMARY BENEFIT

How It Works: Ginger affects the digestive system and brain’s vomiting center, reducing nausea signals through multiple pathways including serotonin receptor antagonism.
Clinical Evidence:
Morning Sickness:
- Meta-analysis of 12 studies: Ginger significantly reduced pregnancy-related nausea by 75%
- 1 gram daily as effective as vitamin B6
- Reduces vomiting episodes by 50%
- Safe during pregnancy (consult healthcare provider)
Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea:
- Study: 0.5-1 gram ginger reduced chemotherapy nausea by 40%
- Works best when taken before treatment
- Complements anti-nausea medications
- Research from Supportive Care in Cancer confirms effectiveness
Motion Sickness:
- More effective than Dramamine in some studies
- Reduces seasickness, car sickness symptoms
- 1 gram taken 30-60 minutes before travel
Post-Surgery Nausea:
- 1 gram before surgery reduces post-operative nausea by 38%
- Decreases need for anti-nausea medications
Dosage for Nausea: 1-1.5 grams fresh ginger or 250-500mg extract, 2-3 times daily
Best Forms: Fresh ginger tea, crystallized ginger, capsules
2. Reduces Inflammation and Inflammatory Markers
Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms: Ginger root benefits include inhibiting COX-2 and 5-LOX enzymes (like NSAIDs), suppressing inflammatory cytokines, and blocking NF-κB inflammatory pathway.
Research Evidence:
- Reduces inflammatory markers (TNF-α, IL-6, CRP) by 15-30%
- Inhibits inflammatory prostaglandin and leukotriene synthesis
- Works on multiple inflammatory pathways simultaneously
- Study in International Journal of Preventive Medicine showed significant inflammatory marker reduction after 45 days
Best For:
- Chronic inflammation
- Metabolic syndrome
- Inflammatory bowel conditions
- Systemic inflammation
Dosage: 1-3 grams fresh ginger or 500-1,000mg extract daily
For comprehensive anti-inflammatory herb comparison, see our anti-inflammatory herbs guide.
3. Relieves Arthritis and Joint Pain
Clinical Studies:
Osteoarthritis:
- Study (2001): Ginger extract reduced knee pain by 40% in 6 weeks
- Comparable effectiveness to ibuprofen in some trials
- Reduces pain and stiffness by 25-50%
- Improves mobility and physical function
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
- Anti-inflammatory effects help manage symptoms
- May reduce disease activity
- Supports conventional treatment (doesn’t replace)
Mechanism: Ginger’s gingerols and shogaols inhibit inflammatory enzymes, reduce joint swelling, and provide analgesic (pain-relieving) effects.
Research Note: A study in Arthritis and Rheumatism found 250mg ginger extract 4 times daily reduced osteoarthritis symptoms significantly.
Dosage for Arthritis: 1-2 grams fresh ginger or 500-1,000mg extract daily, split into 2-3 doses
Timeline: Noticeable improvement in 4-6 weeks with consistent use
4. Reduces Muscle Pain and Soreness
Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage:
Ginger root benefits for athletes include reduced delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS) and faster recovery.
Research Evidence:
- Study: 2 grams ginger daily reduced muscle pain by 25% after exercise
- Decreases muscle soreness progression by 30-50%
- Anti-inflammatory effects support muscle recovery
- Works best when taken consistently (not just post-workout)
Mechanisms:
- Reduces inflammatory response to muscle damage
- Inhibits pain-causing prostaglandins
- May improve muscle recovery time
- Antioxidant protection against exercise-induced oxidative stress
Timing:
- Pre-exercise: 1-2 grams 1 hour before (prevention)
- Daily ongoing: 1-2 grams daily (reduces baseline inflammation)
- Post-exercise: 1-2 grams after workout (recovery support)
Study Reference: Research in Journal of Pain demonstrated 25% reduction in exercise-induced muscle pain.
5. Supports Digestive Health and Function
Beyond nausea relief, ginger root benefits include comprehensive digestive support.
How Ginger Helps Digestion:
✅ Accelerates Gastric Emptying
- Moves food from stomach to small intestine faster
- Reduces bloating and discomfort
- Study: Ginger reduced gastric emptying time from 16 to 12 minutes
✅ Reduces Bloating and Gas
- Carminative properties reduce intestinal gas
- Relaxes gastrointestinal muscles
- Traditional use for flatulence
✅ Supports Enzyme Production
- Stimulates digestive enzyme secretion
- Enhances protein digestion
- Improves nutrient absorption
✅ May Help IBS Symptoms
- Reduces abdominal pain and discomfort
- Anti-inflammatory for gut lining
- Calms intestinal spasms
Dosage for Digestion: 1 gram fresh ginger or 250-500mg extract before or with meals
Best Forms: Fresh ginger tea, ginger chews, crystallized ginger
6. May Lower Blood Sugar and Support Diabetes Management
Metabolic Benefits:
Recent research shows ginger root benefits include improved insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
Clinical Evidence:
Type 2 Diabetes:
- Study: 2 grams ginger powder daily reduced fasting blood sugar by 12%
- Improved insulin sensitivity markers
- Reduced HbA1c (long-term blood sugar marker)
- Study in Complementary Therapies in Medicine showed significant improvements
Mechanisms:
- Increases insulin secretion and sensitivity
- Inhibits enzymes that break down carbohydrates
- Reduces glucose production in liver
- Anti-inflammatory effects reduce metabolic inflammation
Important: Monitor blood sugar if taking diabetes medications—ginger may enhance effects.
Dosage: 2 grams ginger powder daily (under medical supervision if diabetic)
7. Protects Brain Health and Cognitive Function
Neuroprotective Properties:
Ginger root benefits extend to brain health through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms.
Research Evidence:
Cognitive Enhancement:
- Study: Ginger extract improved reaction time and working memory in middle-aged women
- Enhances attention and cognitive processing
- Protects against age-related cognitive decline
Alzheimer’s and Dementia:
- Lab studies: Ginger inhibits amyloid plaque formation
- Reduces brain inflammation (neuroinflammation)
- Antioxidant protection for brain cells
- May slow neurodegenerative progression
Mechanisms:
- Powerful antioxidant (protects neurons from oxidative damage)
- Anti-inflammatory (reduces chronic brain inflammation)
- Increases acetylcholine (memory neurotransmitter)
- Improves blood flow to brain
Research from Evidence-Based Complementary Medicine demonstrates ginger’s neuroprotective potential.
Dosage for Brain Health: 1-2 grams daily (long-term use recommended)
For complementary brain support, consider Lions Mane mushroom.
8. Supports Heart Health and Circulation
Cardiovascular Benefits:
Cholesterol Reduction:
- Study: 3 grams ginger powder daily reduced LDL cholesterol by 10%
- Modest HDL (good cholesterol) increase
- Reduced triglycerides
- Improved cholesterol ratios
Blood Pressure:
- May reduce blood pressure by 5-8 mmHg (modest effect)
- Improves arterial function
- Vasodilator properties (relaxes blood vessels)
Blood Thinning:
- Mild antiplatelet effects (reduces clotting)
- May complement aspirin therapy
- Caution: May increase bleeding risk at high doses
Antioxidant Protection:
- Prevents LDL oxidation (key step in atherosclerosis)
- Protects blood vessels from damage
- Reduces cardiovascular inflammation
Dosage: 2-3 grams fresh ginger or 500-750mg extract daily
Important: Consult healthcare provider if on blood thinners or before surgery.
9. May Have Anti-Cancer Properties
Disclaimer: Ginger should NEVER replace conventional cancer treatment. Research suggests potential complementary benefits.
Laboratory and Animal Research:
Anti-Cancer Mechanisms:
- Induces apoptosis (cancer cell death)
- Inhibits cancer cell proliferation
- Anti-inflammatory (reduces cancer-promoting inflammation)
- Antioxidant (protects DNA from damage)
Cancers Studied:
- Colorectal cancer (most research)
- Ovarian cancer
- Pancreatic cancer
- Breast cancer
Human Studies (Limited):
- Small study: Ginger reduced inflammation markers in colon cancer risk patients
- May reduce chemotherapy-induced nausea (established benefit)
- Population studies: High ginger consumption correlates with lower cancer rates
Research from British Journal of Nutrition shows promising anti-cancer activity in cell studies.
Status: Promising but needs more human clinical trials
Dosage (Research): 2-4 grams daily (under medical supervision)
10. Supports Weight Loss and Metabolism

Metabolic Effects:
Ginger root benefits include modest support for weight management through multiple mechanisms.
How It Helps:
- Increases thermogenesis (calorie burning) by 5-10%
- Reduces appetite and increases satiety
- Improves fat metabolism
- Reduces inflammation associated with obesity
Research Evidence:
- Meta-analysis: Ginger supplementation led to significant weight and waist circumference reduction
- Improves metabolic markers (cholesterol, blood sugar)
- Enhances fat oxidation during exercise
Realistic Expectations: Ginger is a supportive tool, not a magic weight loss solution. Effects are modest and work best combined with diet and exercise.
Dosage: 2 grams powder or 500-750mg extract daily
Study from Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition confirms metabolic benefits.
11. Reduces Menstrual Pain (Dysmenorrhea)
Clinical Evidence:
Ginger is highly effective for menstrual cramps, comparable to common pain medications.
Research:
- Study: Ginger as effective as ibuprofen for menstrual pain
- 250mg ginger 4 times daily reduced pain by 60%
- Reduces pain intensity and duration
- Works best when started at onset of menstruation
Mechanisms:
- Inhibits prostaglandins (cause uterine cramping)
- Anti-inflammatory for pelvic inflammation
- Muscle relaxant properties
Dosage for Menstrual Pain: 250-500mg ginger extract 3-4 times daily during menstruation, or 1 gram fresh ginger 3x daily
Timing: Start at first sign of menstruation or 1 day before expected start
Research published in Pain Medicine confirms effectiveness.
12. Antimicrobial and Immune Support
Antimicrobial Properties:
Ginger shows activity against various pathogens:
Antibacterial:
- Effective against oral bacteria (Streptococcus mutans)
- May help prevent dental infections
- Activity against E. coli and other bacteria
Antiviral:
- May reduce viral respiratory infections
- Supports immune response to colds and flu
- Traditional use for respiratory illness
Antifungal:
- Activity against Candida species
- May help with fungal infections
Immune Enhancement:
- Stimulates immune cell activity
- Anti-inflammatory support for immune function
- Antioxidant protection for immune cells
Dosage for Immune Support: 1-2 grams fresh ginger daily, or ginger tea 2-3 times daily
For comprehensive immune support, combine with turkey tail mushroom.
Fresh Ginger vs Dried Ginger vs Ginger Extract
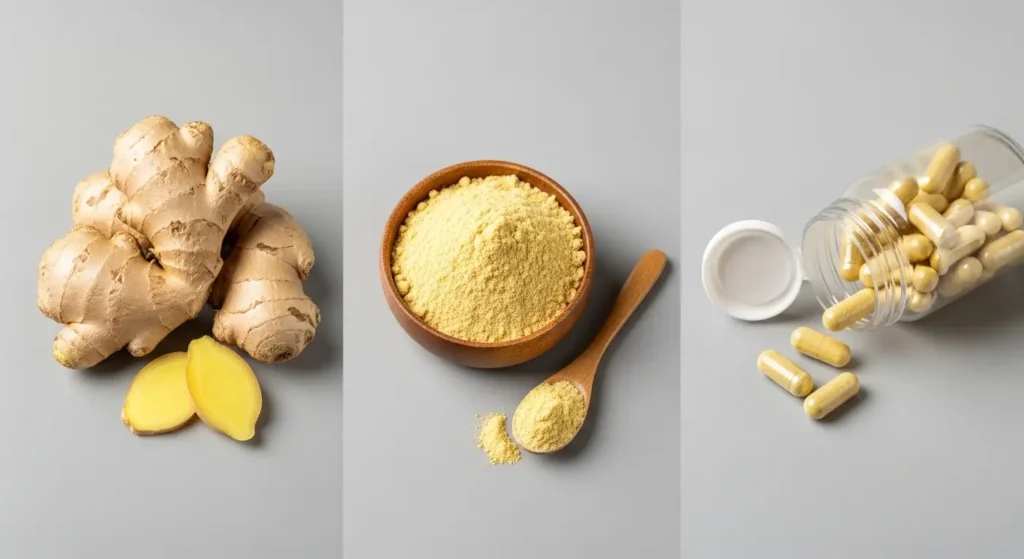

Fresh Ginger Root
Characteristics:
- High in gingerols (pungent, fresh compounds)
- Milder, zingier flavor
- Best for nausea, digestion
- More volatile oils (aromatic)
Best Uses:
- Ginger tea
- Cooking and juicing
- Fresh ginger shots
- Immediate digestive relief
Dosage: 1-3 grams daily (1-inch piece ≈ 5 grams)
Pros: Whole food, versatile, fresh taste Cons: Perishable, less concentrated, variable potency
Dried Ginger Powder
Characteristics:
- High in shogaols (heating converts gingerols)
- More concentrated and pungent
- Better for pain and inflammation
- Longer shelf life
Best Uses:
- Capsules and supplements
- Baking and cooking
- Golden milk recipes
- Long-term storage
Dosage: 1-3 grams daily
Pros: Concentrated, shelf-stable, higher shogaol content Cons: Stronger taste, different compound profile than fresh
Ginger Extract/Supplements
Characteristics:
- Standardized gingerol content (typically 5%)
- Most concentrated form
- Precise dosing
- No taste
Best Uses:
- Clinical/therapeutic doses
- Convenience and travel
- Consistent potency
- When avoiding ginger taste
Dosage: 250-1,000mg extract daily (follow product instructions)
Pros: Standardized, convenient, no taste, precise dosing Cons: Processed, more expensive, may contain fillers
How Much Ginger Should You Take?
Dosage by Condition
| Condition | Ginger Dosage | Form | Timing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nausea (General) | 1-1.5g | Fresh/tea/capsules | 2-3x daily as needed |
| Morning Sickness | 1g | Fresh/capsules | Divided doses daily |
| Motion Sickness | 1g | Fresh/capsules | 30-60 min before travel |
| Arthritis/Joint Pain | 1-2g | Fresh/extract | 2-3x daily with meals |
| Muscle Soreness | 2g | Powder/extract | Daily ongoing |
| Digestive Issues | 1g | Fresh/tea | Before or with meals |
| Blood Sugar | 2g | Powder | Daily with meals |
| Menstrual Cramps | 250-500mg extract | Capsules | 3-4x daily during period |
| General Wellness | 1-2g | Fresh/tea/powder | Daily |
General Guidelines:
- Start with lower doses and increase gradually
- Doses up to 4 grams daily generally safe
- Higher doses (>5g) may cause digestive upset
- Split larger doses throughout the day
How to Take Ginger: Best Methods
1. Fresh Ginger Tea (Most Popular)
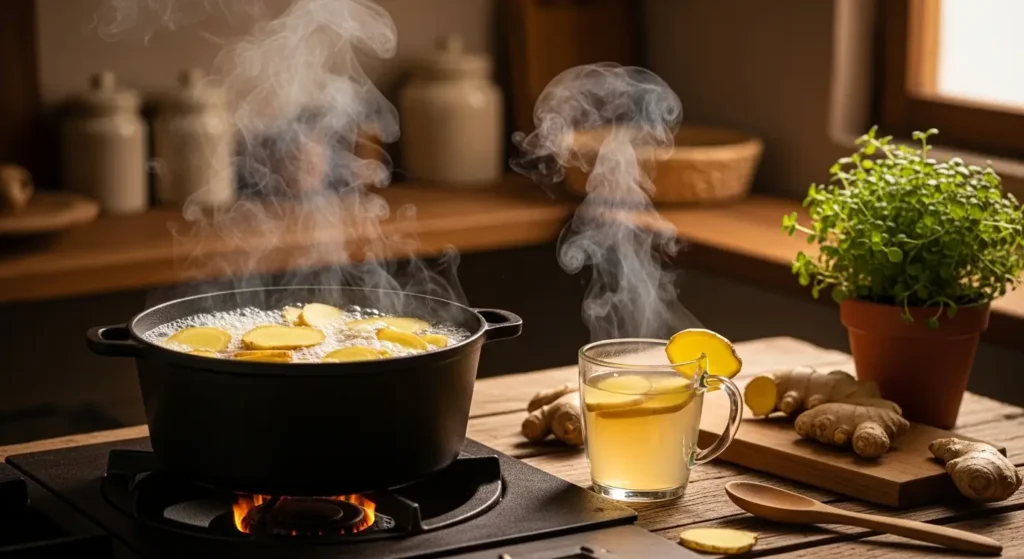

Recipe:
Ingredients:
- 1-2 inches fresh ginger (thinly sliced or grated)
- 2 cups water
- Honey and lemon (optional)
Instructions:
1. Bring water to boil
2. Add ginger slices
3. Simmer 10-15 minutes
4. Strain, add honey/lemon if desired
5. Drink warm
Best For: Nausea, digestion, immune support, general wellness
2. Ginger Shots
Recipe:
- 2-3 inches fresh ginger
- 1/2 lemon, juiced
- Pinch cayenne (optional)
- Small amount honey (optional)
Blend or juice, drink immediately
Best For: Concentrated dose, immune boost, morning energy
3. Ginger Capsules/Supplements
Dosage: Follow product instructions (typically 250-1,000mg daily)
Best For: Consistent dosing, convenience, avoiding ginger taste, therapeutic use
See our best turmeric supplements review for combination turmeric-ginger products.
4. Crystallized/Candied Ginger
Amount: 2-3 pieces (about 10-15g)
Best For: Nausea, motion sickness, travel, pleasant taste
Note: Contains sugar—not ideal for diabetes or weight loss
5. Ginger in Cooking
Amount: 1-2 teaspoons fresh grated or 1/2-1 teaspoon powder in meals
Best For: Daily culinary use, anti-inflammatory benefits, flavor
Ginger Safety and Side Effects

General Safety
Ginger is very safe for most people at recommended doses. Used medicinally for 5,000+ years with excellent safety record.
Mild Side Effects (Rare):
- Heartburn or acid reflux (high doses, sensitive individuals)
- Mild stomach upset or diarrhea (excessive doses >5g)
- Bloating or gas (uncommon)
- Mild skin irritation (topical use)
Who Should Be Cautious
Pregnancy:
- Generally safe at 1 gram daily for morning sickness
- Higher doses not well-studied
- Consult healthcare provider
- Avoid close to delivery (theoretical bleeding risk)
Blood Thinners:
- May enhance anticoagulant effects
- Caution with warfarin, aspirin, clopidogrel
- Monitor INR if on warfarin
- Increased bleeding risk at doses >4g daily
Before Surgery:
- Stop ginger 1-2 weeks before surgery
- Inform surgical team
- Bleeding risk concern
Gallstones:
- Ginger stimulates bile production
- May cause discomfort if bile ducts blocked
- Consult healthcare provider
Diabetes Medications:
- May lower blood sugar
- Monitor glucose levels
- May need medication adjustment
Low Blood Pressure:
- May lower blood pressure further
- Monitor if hypotensive
Drug Interactions
Blood Thinners (Important):
- Warfarin, aspirin, clopidogrel
- May increase bleeding risk
- Coordinate with healthcare provider
Diabetes Medications:
- May enhance blood sugar-lowering
- Monitor glucose carefully
Blood Pressure Medications:
- May enhance blood pressure-lowering
- Monitor blood pressure
General Rule: Inform healthcare providers about ginger use, especially before procedures or if on medications.
Ginger vs Turmeric: Which Is Better?

Both are powerful anti-inflammatory herbs from the same family. Here’s how they compare:
Ginger Advantages:
- ✅ Superior for nausea (ginger wins decisively)
- ✅ Better for digestive issues (more immediate relief)
- ✅ Excellent for muscle soreness
- ✅ Pleasant taste (easier to consume fresh)
- ✅ Works faster for acute symptoms
Turmeric Advantages:
- ✅ More powerful overall anti-inflammatory (curcumin)
- ✅ Better for chronic inflammation
- ✅ More extensive research (13,000+ studies)
- ✅ Superior for arthritis (with enhanced bioavailability)
- ✅ Brain and heart benefits more established
Best Approach: Use both! They’re highly complementary and often combined in supplements and recipes.
For detailed comparison, see our turmeric vs ginger guide.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What are the main ginger root benefits?
Ginger’s primary benefits include powerful nausea relief (75% reduction), anti-inflammatory effects comparable to NSAIDs, pain reduction for arthritis and muscle soreness (25-50%), digestive support, blood sugar regulation, brain protection, and cardiovascular health. It’s backed by over 500 scientific studies.
-
How much ginger should I take daily?
For general wellness: 1-2 grams fresh ginger or 250-500mg extract daily. For nausea: 1-1.5 grams 2-3 times daily. For arthritis/pain: 1-2 grams divided into 2-3 doses. For blood sugar: 2 grams daily. Maximum generally safe dose: 4 grams daily. Start low and increase gradually.
-
Is fresh ginger better than ginger powder?
Fresh ginger has more gingerols (better for nausea and digestion). Dried ginger has more shogaols (better for pain and inflammation). Both are beneficial—choose based on your goal. Fresh for digestive issues, dried/extract for anti-inflammatory and pain relief.
-
Can I take ginger every day?
Yes, daily ginger consumption is safe for most people at doses up to 4 grams. Traditional use and clinical studies support long-term daily use. Take with food if experiencing any digestive discomfort.
-
How long does ginger take to work?
For nausea: 30-60 minutes. For digestion: Within 1-2 hours. For pain/inflammation: 2-4 weeks of consistent use for noticeable improvement. For chronic conditions (arthritis, blood sugar): 4-8 weeks for maximum benefits. Consistency is key.
-
Can ginger help you lose weight?
Ginger provides modest weight loss support by increasing metabolism (5-10%), reducing appetite, and improving fat oxidation. However, effects are small—it’s a supportive tool, not a magic solution. Works best combined with healthy diet and exercise. Typical effect: 1-2 pounds additional loss over several months.
-
Is ginger good for inflammation?
Yes, ginger is an excellent anti-inflammatory herb. It inhibits COX-2 and LOX enzymes (like NSAIDs) and reduces inflammatory markers by 15-30%. Clinical studies show effectiveness for arthritis, muscle soreness, and chronic inflammation comparable to ibuprofen in some cases. See our anti-inflammatory herbs guide for comparisons.
-
Can I take ginger and turmeric together?
Yes, ginger and turmeric are highly complementary and often combined for synergistic anti-inflammatory effects. They work through different mechanisms, enhancing overall benefits. Common in supplements and golden milk recipes. Both are from the same plant family and safe to combine. Learn more in our turmeric benefits guide.
The Bottom Line on Ginger Root Benefits
Ginger root benefits are extensive and well-supported by over 500 scientific studies, making it one of the most versatile medicinal herbs available. From powerful nausea relief to anti-inflammatory effects, pain reduction, and metabolic support, ginger provides evidence-based therapeutic benefits with excellent safety.
Key Takeaways:
- ✅ Most powerful benefit: Nausea relief (75% reduction, superior to many drugs)
- ✅ Best for: Nausea, digestion, arthritis, muscle soreness, inflammation
- ✅ Effective dose: 1-2 grams fresh ginger or 250-1,000mg extract daily
- ✅ Timeline: Nausea relief in 30-60 min, pain relief in 2-4 weeks
- ✅ Safety: Excellent safety profile, safe for long-term daily use
- ✅ Forms: Fresh (best for nausea/digestion), dried/extract (best for pain/inflammation)
Getting Started:
- Choose form based on goal (fresh for digestion, extract for pain)
- Start with 1 gram daily and increase as needed
- Take with food if experiencing any digestive discomfort
- Be consistent—benefits build over time
- Combine with turmeric for enhanced anti-inflammatory effects
Ready to experience ginger root benefits?
- Start with simple ginger tea (1-2 inches fresh ginger, simmered 10-15 minutes)
- Or try ginger supplements for precise dosing
- Combine with turmeric for comprehensive anti-inflammatory support
Looking for more natural anti-inflammatory options?
- Anti-Inflammatory Herbs Guide – 12 powerful herbs
- Turmeric Curcumin Benefits – Comprehensive guide
- Turmeric vs Ginger – Which is better?
- Best Turmeric Supplements – Many include ginger
Medical Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. Ginger root benefits, dosages, and uses should be discussed with qualified healthcare providers, especially if you have medical conditions, take medications (particularly blood thinners), are pregnant/nursing, or before surgery.
Last Updated: January 2026





